The Silent Threat: Recognizing the Early Signs of Oral Cancer
Many people tend to dismiss small or seemingly harmless changes in their mouths—believing that a sore, a discolored patch, or mild numbness is nothing serious. However, such symptoms can sometimes be early warning signs of a far more dangerous disease: oral cancer. This condition often develops quietly, showing little to no symptoms in its early stages. By the time it becomes noticeable, it may already have reached an advanced and difficult-to-treat stage.
Risk and High-Risk Groups
Individuals over the age of 40—particularly those who smoke or consume alcohol regularly—are at higher risk. Even mild or persistent symptoms like mouth sores, swelling, or difficulty swallowing should never be ignored. Early detection and timely treatment can mean the difference between life and death.
Understanding Oral Cancer and Its Prevalence in India
Oral cancer can affect different parts of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, palate, and the floor of the mouth. In India, more than 77,000 new cases are diagnosed every year, with over 52,000 deaths—making it one of the country’s leading causes of cancer-related deaths.
A major challenge is late diagnosis. Oral cancer is often discovered only after it has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. Yet, when detected early, the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival increase dramatically. Raising awareness, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and paying attention to warning signs are essential steps toward prevention.
Types of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is not confined to one location—it can develop in various parts of the oral cavity, including:
-
Lip cancer
-
Tongue cancer
-
Gum cancer
-
Inner cheek (buccal mucosa) cancer
-
Floor of the mouth cancer
-
Hard and soft palate cancer
Each type presents unique symptoms, but all require immediate medical evaluation once warning signs appear.
When to See a Specialist
If you notice any unusual symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a dentist or oral cancer specialist without delay. Routine oral examinations should ideally be conducted twice a year, even in the absence of visible problems. Specialists such as Dr. Sajjan Rajpurohit, a renowned oncologist in Delhi, emphasize early detection and customized treatment plans, which significantly improve patient outcomes.
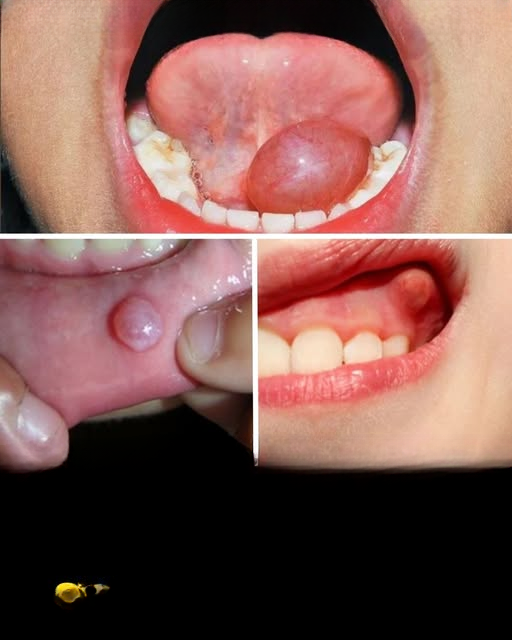
Common Symptoms of Oral Cancer
In its early stages, oral cancer may not produce noticeable signs, making vigilance especially important for those in high-risk groups. Look out for:
-
Sores or blisters in the mouth that persist or fail to heal
-
Red or white patches on the lips, gums, or inside the mouth
-
Lumps, swelling, or thickening in the mouth or neck
-
Unexplained bleeding
-
Loose teeth without dental cause
-
Pain or difficulty while chewing or swallowing
-
Numbness in the lips, tongue, chin, or neck
-
Persistent sore throat or hoarseness
-
Sudden, unexplained weight loss
-
Jaw stiffness or pain
-
Ear pain without hearing issues
-
Chronic dry mouth or burning sensations
-
Tongue discomfort or pain
If any of these symptoms persist for more than two weeks, seek professional evaluation—especially if they do not respond to regular treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several key factors can increase the likelihood of developing oral cancer:
-
Tobacco use: Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and chewing tobacco are responsible for nearly 80% of oral cancer cases.
-
Excessive alcohol consumption: The risk multiplies when combined with tobacco use.
-
HPV infection: Certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) are linked to oral cancers, particularly those affecting the throat.
-
Poor oral hygiene: Neglecting oral health over time can heighten vulnerability to infections and cancer.
-
Sun exposure: Long-term, unprotected exposure to sunlight increases the risk of lip cancer.
-
Family history: Genetic predisposition can raise susceptibility in some individuals.
-
Nutritional deficiencies: Diets lacking fruits and vegetables may weaken the body’s natural defenses against cancer.
Stages of Oral Cancer
Understanding the stages of oral cancer helps determine appropriate treatment and prognosis:
-
Stage 1: Tumor is less than 2 cm and has not spread to lymph nodes.
-
Stage 2: Tumor measures 2–4 cm but remains localized.
-
Stage 3: Tumor exceeds 4 cm or has spread to a nearby lymph node.
-
Stage 4: Cancer has metastasized to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or distant organs—making treatment more complex.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cancer’s type, location, and stage. The main approaches include:
-
Surgery: The first line of treatment, often followed by reconstructive procedures using techniques such as pedicle or free flap reconstruction.
-
Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. Options include external beam radiation (EBRT) and brachytherapy (localized internal radiation).
-
Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs target and kill cancer cells, often used alongside radiation for better effectiveness.
-
Targeted therapy: Focuses on specific molecules that promote cancer growth, typically with fewer side effects than standard chemotherapy.
-
Immunotherapy: In advanced cases, boosts the immune system’s ability to attack cancer cells.
A multidisciplinary approach, combining surgery, radiation, and drug therapy, often produces the most effective results.
Key Facts and Statistics
-
Over 80% of oral cancer cases are preventable through lifestyle changes.
-
The average age of diagnosis is around 50, though younger individuals—especially those exposed to HPV—are increasingly affected.
-
Men are twice as likely as women to develop oral cancer.
-
Early detection raises the survival rate to 82%, while late-stage detection drops it to 27%.
-
Regular screenings can detect abnormalities long before symptoms appear.
Why Early Detection Matters
In countries like India, oral cancer often goes unnoticed until advanced stages—largely due to limited awareness, delayed consultations, and inadequate access to specialized care in rural regions. Educating the public and promoting regular dental visits are essential to changing this trend.
By staying alert to early warning signs, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking prompt medical care, individuals can greatly increase their chances of recovery and reduce life-threatening complications.
Conclusion
Oral cancer is a silent yet deadly disease that can affect anyone. Fortunately, it is also one of the most preventable and treatable cancers when detected early. Persistent sores, unusual patches, swallowing difficulties, or any unexplained changes in the mouth should never be ignored.
Regular dental check-ups, awareness of risk factors, and early screening are powerful tools in preventing and combating this disease. Being proactive is the strongest defense against oral cancer—and the key to safeguarding your health and future.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for any health concerns or symptoms.